# 旋转物体检测数据roLabelImg转DOTA格式
roLabelImg 工具仓库地址:https://github.com/cgvict/roLabelImg (opens new window)
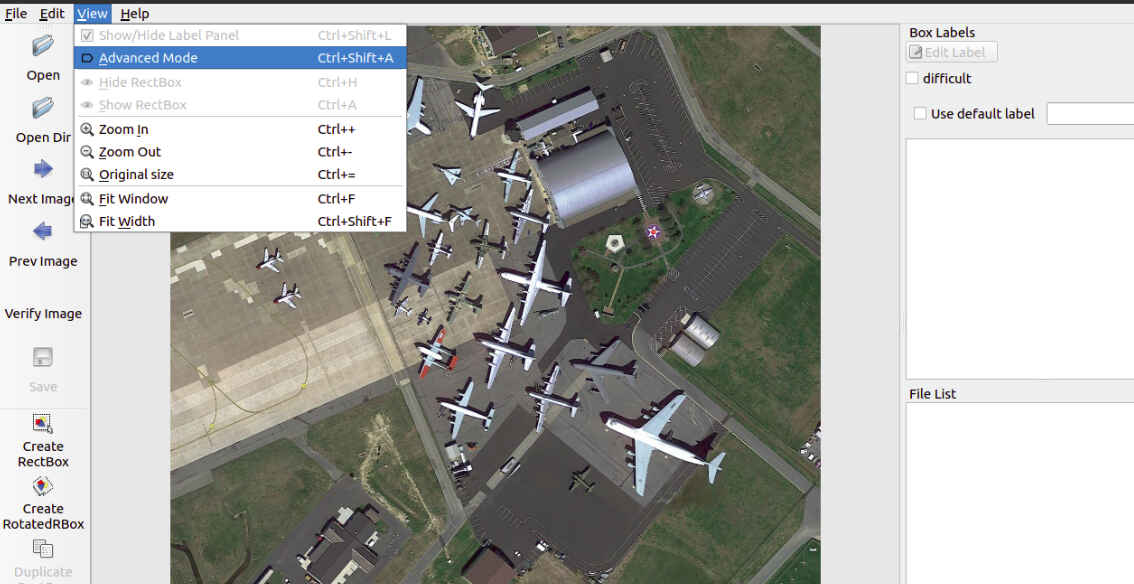
# 1.进入可以画旋转检测框的模式
# 2.标注文件样式
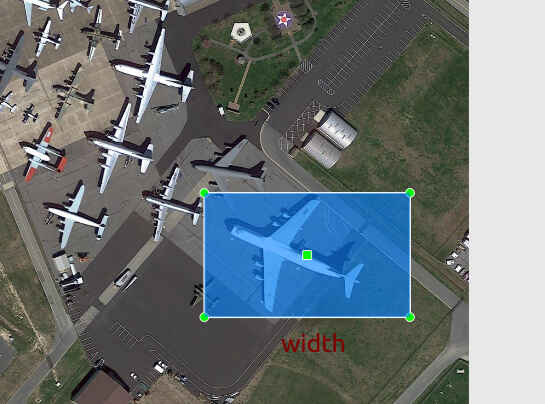
roLabelImg标注旋转检测框时是先画一个常规的矩形框,然后绕矩形的中心点顺时针和逆时针旋转一定的角度来实现的。标注文件中对旋转检测框的定义是使用(cx, cy, width, height, angle)的格式定义的,如下:
<robndbox>
<cx>1178.4388</cx>
<cy>1004.6478</cy>
<w>319.635</w>
<h>273.2016</h>
<angle>0.46</angle>
</robndbox>
(cx, cy)是旋转框的中心点像素坐标,w的定义是在roLabelImg中画初始矩形框时在图像x方向上的边长, 另一条边是h,画好初始矩形后,无论后续如何旋转,w和h所指的边都不会变。angle角的定义是旋转矩形检测框的w边和X轴正方向顺时针所成的角度,其大小为[0,pi)
初始矩形检测框:
调整姿态后检测框:
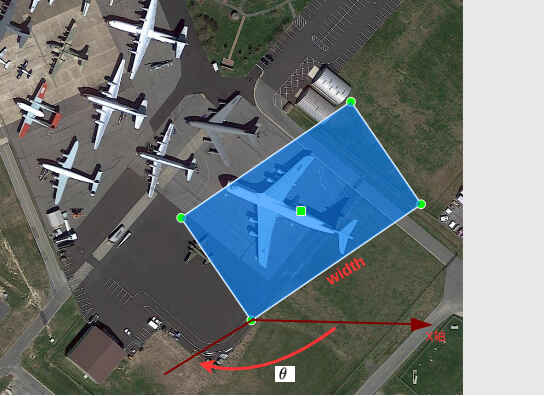
其中2.541593。
# 3.DOTA数据格式
DOTA是武汉大学开源的旋转物体检测数据集,其主页见https://captain-whu.github.io/DOTA/dataset.html (opens new window)。DOTA标注文件的格式为:
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4, category, difficult
(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4)分别是旋转物体检测框的四个顶点的坐标,category是检测框物体对象的类别
# 4.roLabelImg标注文件转DOTA格式
大多数旋转物体检测的开源算法的数据处理部分都支持DOTA格式,如商汤开源的mmrotate (opens new window),为了更快的在自己数据集上验证算法的有效性,最方便的算法就是将roLabelImg标注的xml文件转成上述的标签格式,roLabelImg标注文件转DOTA可分成四种情况。
- 1)
- 2)
- 3)
- 4)


A(x1, y1),B(x3, y3),D(x2, y2),E(x4, y4)点的坐标由上述三角形之间的关系可以求得:
同样可以求其他三种情况。
转换代码见:
def convert_rolabelimg2dota(xml_path:str) -> None:
"""
Args:
- `xml_path` (str) : path to roLabelImg label file, like /xx/xx.xml
Returns:
- `box_points` (list): shape (N, 8 + 1), N is the number of objects, 8 + 1 is \
`(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4, class_name)`
"""
with open(xml_path) as f:
tree = ET.parse(f)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
width = int(size.find('width').text)
height = int(size.find('height').text)
objects = root.iter('object')
boxes = [] # list of tuple(cz, cy, w, h, angle), angle is in [0-pi)
for obj in objects:
if obj.find('type').text == 'robndbox':
rbox_node = obj.find('robndbox')
cat = obj.find('name').text
rbox = dict()
for key in ['cx', 'cy', 'w', 'h', 'angle']:
rbox[key] = float(rbox_node.find(key).text)
boxes.append(list((*rbox.values(), cat)))
print(f"bboxes: {boxes}")
box_points = [] # list of box defined with four vertices
for box in boxes:
cx, cy, w, h, ag, cat = box
alpha_w = math.atan(w / h)
alpha_h = math.atan(h / w)
d = math.sqrt(w**2 + h**2) / 2
if ag > math.pi / 2:
beta = ag - math.pi / 2 + alpha_w
if beta <= math.pi / 2:
x1, y1 = cx + d * math.cos(beta), cy + d * math.sin(beta)
x2, y2 = cx - d * math.cos(beta), cy - d * math.sin(beta)
elif beta > math.pi / 2:
beta = math.pi - beta
x1, y1 = cx - d * math.cos(beta), cy + d * math.sin(beta)
x2, y2 = cx + d * math.cos(beta), cy - d * math.sin(beta)
x3, y3 = x1 - h * math.cos(ag - math.pi / 2), y1 - h * math.sin(ag - math.pi / 2)
x4, y4 = x2 + h * math.cos(ag - math.pi / 2), y2 + h * math.sin(ag - math.pi / 2)
elif ag <= math.pi / 2:
beta = ag + alpha_h
if beta <= math.pi / 2:
x1, y1 = cx + d * math.cos(beta), cy + d * math.sin(beta)
x2, y2 = cx - d * math.cos(beta), cy - d * math.sin(beta)
elif beta > math.pi / 2:
beta = math.pi - beta
x1, y1 = cx - d * math.cos(beta), cy + d * math.sin(beta)
x2, y2 = cx + d * math.cos(beta), cy - d * math.sin(beta)
x3, y3 = x1 - w * math.cos(ag), y1 - w * math.sin(ag)
x4, y4 = x2 + w * math.cos(ag), y2 + w * math.sin(ag)
points = np.array([x1, y1, x3, y3, x2, y2, x4, y4], dtype=np.int32)
points[0::2] = np.clip(points[0::2], 0, width)
points[1::2] = np.clip(points[1::2], 0, height)
box_points.append([*points, cat])
return box_points
完整代码见gitee仓库object_detection_task (opens new window)