# Otsu阈值法原理及实现
# Otsu算法简介
Otsu阈值法发表于1979年,论文为A threshold selection method from gray level histograms (opens new window),作者是日本东京大学的Nobuyuki Otsu(大津 展之)。
自动全局阈值算法通常包括如下几步
- 1.对输入图像进行预处理,如高斯平滑
- 2.获取图像的灰度直方图
- 3.计算阈值T
- 4.对原图像二值化,小于阈值T的位置像素值设为0,大于阈值T的像素值设为255
一般,各种阈值处理算法的区别主要在第3步,即确定阈值的逻辑不同。
# Otsu 算法的逻辑
其核心思想是,将图像的像素根据某个像素值分成两簇,并使得这两簇之间的像素值的类间方差最大化。
所以Otsu算法适合用于像素直方图表现为双峰图像的阈值处理。
双峰图像(bimodal images)是指具有如下形式像素直方图的图像:
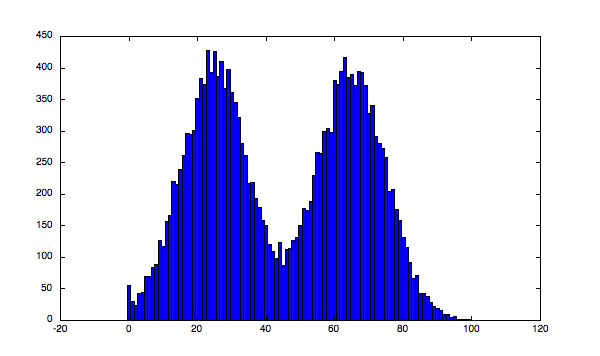
如下就是一个双峰图像的示例:

假设一副灰度图,像素值灰度级为
像素值为第
基于上述假设,某个像素点为灰度级
取灰度级
对于图像中某个像素属于
求
同样可推导:
整幅图像的像素均值记为:
求
同样可推导:
为了衡量所取阈值
类内方差:
类间方差:
图像总的像素值方差:
可以推导三者之间有如下关系:
从上面的定义可以发现,
上面
# 源码实现
// Include Libraries
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(){
// read the image in BGR format
Mat testImage = imread("boat.jpg", 0);
int bins_num = 256;
// Get the histogram
long double histogram[256];
// initialize all intensity values to 0
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
histogram[i] = 0;
// calculate the no of pixels for each intensity values
for(int y = 0; y < testImage.rows; y++)
for(int x = 0; x < testImage.cols; x++)
histogram[(int)testImage.at<uchar>(y,x)]++;
// Calculate the bin_edges
long double bin_edges[256];
bin_edges[0] = 0.0;
long double increment = 0.99609375;
for(int i = 1; i < 256; i++)
bin_edges[i] = bin_edges[i-1] + increment;
// Calculate bin_mids
long double bin_mids[256];
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
bin_mids[i] = (bin_edges[i] + bin_edges[i+1])/2;
// Iterate over all thresholds (indices) and get the probabilities weight1, weight2
long double weight1[256];
weight1[0] = histogram[0];
for(int i = 1; i < 256; i++)
weight1[i] = histogram[i] + weight1[i-1];
int total_sum=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
total_sum = total_sum + histogram[i];
long double weight2[256];
weight2[0] = total_sum;
for(int i = 1; i < 256; i++)
weight2[i] = weight2[i-1] - histogram[i - 1];
// Calculate the class means: mean1 and mean2
long double histogram_bin_mids[256];
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
histogram_bin_mids[i] = histogram[i] * bin_mids[i];
long double cumsum_mean1[256];
cumsum_mean1[0] = histogram_bin_mids[0];
for(int i = 1; i < 256; i++)
cumsum_mean1[i] = cumsum_mean1[i-1] + histogram_bin_mids[i];
long double cumsum_mean2[256];
cumsum_mean2[0] = histogram_bin_mids[255];
for(int i = 1, j=254; i < 256 && j>=0; i++, j--)
cumsum_mean2[i] = cumsum_mean2[i-1] + histogram_bin_mids[j];
long double mean1[256];
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
mean1[i] = cumsum_mean1[i] / weight1[i];
long double mean2[256];
for(int i = 0, j = 255; i < 256 && j >= 0; i++, j--)
mean2[j] = cumsum_mean2[i] / weight2[j];
// Calculate Inter_class_variance
long double Inter_class_variance[255];
long double dnum = 10000000000;
for(int i = 0; i < 255; i++)
Inter_class_variance[i] = ((weight1[i] * weight2[i] * (mean1[i] - mean2[i+1])) / dnum) * (mean1[i] - mean2[i+1]);
// Maximize interclass variance
long double maxi = 0;
int getmax = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 255; i++){
if(maxi < Inter_class_variance[i]){
maxi = Inter_class_variance[i];
getmax = i;
}
}
cout << "Otsu's algorithm implementation thresholding result: " << bin_mids[getmax];