# 基于分割的文本检测算法--DBNet++
# 1.概况
2022年02月份论文:Real-Time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization and Adaptive Scale Fusion (opens new window)
DBNet是2019年11月华中科技大学的Xiang Bai等提出的方法,其详细介绍见4.基于分割的文本检测算法--DBNet (opens new window)
DBNet++是原作者团队基于DBNet的改进工作,是DBNet会议论文的期刊版,除了DBNet中已经介绍过的可微分二值化运算之外,DBNet++中的主要创新是自适应多尺度特征融合(Adapptive Scale Fusion,ASF)模块的提出。
在以往的分割算方法中,多尺度特征图大都是通过FPN后直接进行concatenate来实现,这样做并没有考虑不同尺度特征图的重要性是不一样的。本文中,作者提出的自适应特征图融合模块使用了空间注意力机制,具体的介绍见第2部分。
# 2.DBNet++中的主要方法
# 2.1 网络结构
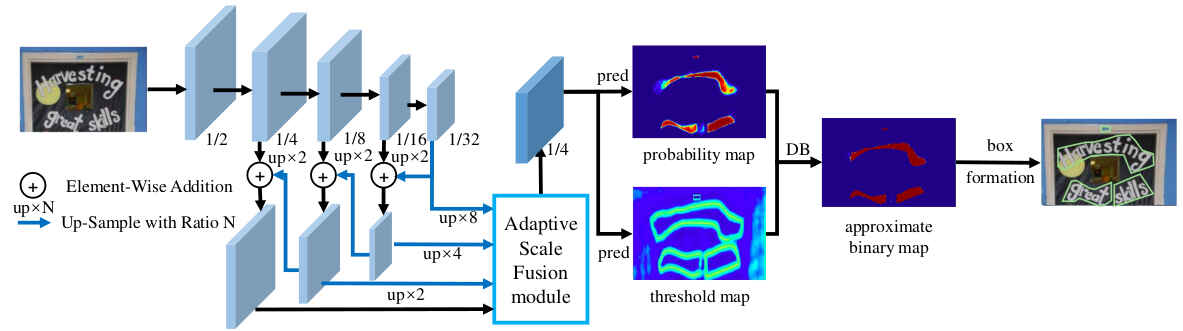
如上图所示,DBNet++的网络结构几乎相同,使用FPN的backbone,可微分二值化,基于分割概率图求文本区域等,主要的不同在对backbone上输出的特征图的处理上,DBNet++中新引入了Adaptive Scale Fusion模块。
# 2.2 适应特征图融合模块(Adaptive Scale Fusion Module, ASF)
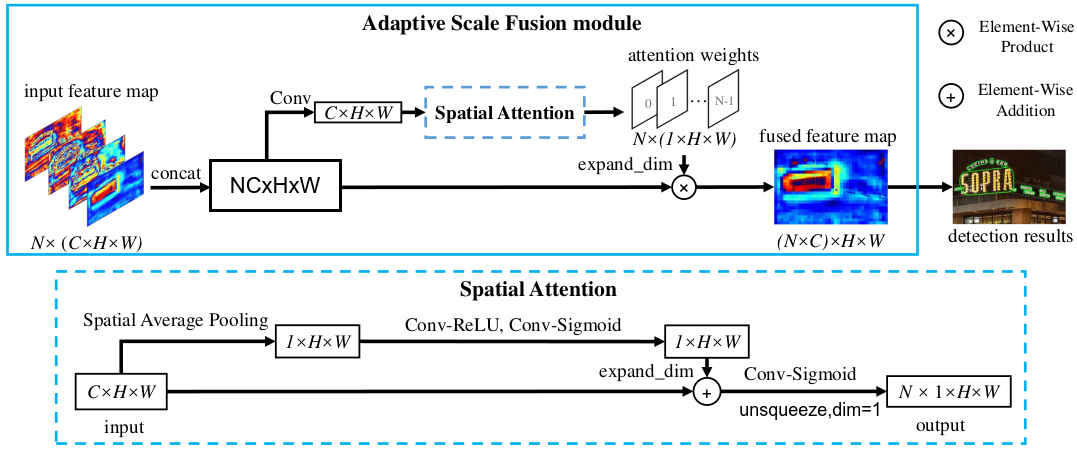
图中对一个特征图的shape描述进行了修改,原论文图中存在特征图shape从N×C×H×W经过conv后变成C×H×W容易引起误解(容易误会成卷积将四维向量变成了三维)。
计算过程如上图所示,值的注意的是空间注意力机制的使用,先是对每个通道取均值得到特征图每个像素位置上的重要性,再将其加到原输入特征图上,增强每个位置的特征值,再通过卷积输出通道为N个的注意力权重,使得输出的权重能衡量每个尺度特征图的重要性。
backbone提取后输入到 ASF的特征图为
先将N个特征图 concatenate到一起,然后再经过一个concatenate到一起就得到了 ASF的输出。
# 3.ASF模块的源码实现
decoders/feature_attention.py
class ScaleSpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, num_features, init_weight=True):
super(ScaleSpatialAttention, self).__init__()
self.spatial_wise = nn.Sequential(
#Nx1xHxW
nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, bias=False, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.attention_wise = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, num_features, 1, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
if init_weight:
self._initialize_weights()
...
def forward(self, x):
global_x = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
global_x = self.spatial_wise(global_x) + x
global_x = self.attention_wise(global_x)
return global_x
class ScaleFeatureSelection(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels , out_features_num=4, attention_type='scale_spatial'):
super(ScaleFeatureSelection, self).__init__()
self.in_channels=in_channels
self.inter_channels = inter_channels
self.out_features_num = out_features_num
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, inter_channels, 3, padding=1)
self.type = attention_type
if self.type == 'scale_spatial':
self.enhanced_attention = ScaleSpatialAttention(inter_channels, inter_channels//4, out_features_num)
elif self.type == 'scale_channel_spatial':
self.enhanced_attention = ScaleChannelSpatialAttention(inter_channels, inter_channels // 4, out_features_num)
elif self.type == 'scale_channel':
self.enhanced_attention = ScaleChannelAttention(inter_channels, inter_channels//2, out_features_num)
def _initialize_weights(self, m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data)
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
m.weight.data.fill_(1.)
m.bias.data.fill_(1e-4)
def forward(self, concat_x, features_list):
concat_x = self.conv(concat_x)
score = self.enhanced_attention(concat_x)
assert len(features_list) == self.out_features_num
if self.type not in ['scale_channel_spatial', 'scale_spatial']:
shape = features_list[0].shape[2:]
score = F.interpolate(score, size=shape, mode='bilinear')
x = []
for i in range(self.out_features_num):
x.append(score[:, i:i+1] * features_list[i])
return torch.cat(x, dim=1)