# 0.简介
Batch Normalization在训练过程中对网络的输入输出进行归一化,可有效防止梯度爆炸和梯度消失,能加快网络的收敛速度。
如上式,x表示的是输入变量,E(x)和Var(x)分别表示x的那每个特征维度在batch size上所求得的梯度及方差。1e-5,torch BatchNorm API中,可通过设置affine=True/False来设置这两个参数是固定还是可学习的。True表示可学习,False表示不可学习,默认
# 1.BatchNorm1d
BatchNorm1d是对NXC或NXCXL维度的向量做Batch Normalization,N表示Batch Size的大小,C表示数据的维度,L表示每个维度又有多少维组成。
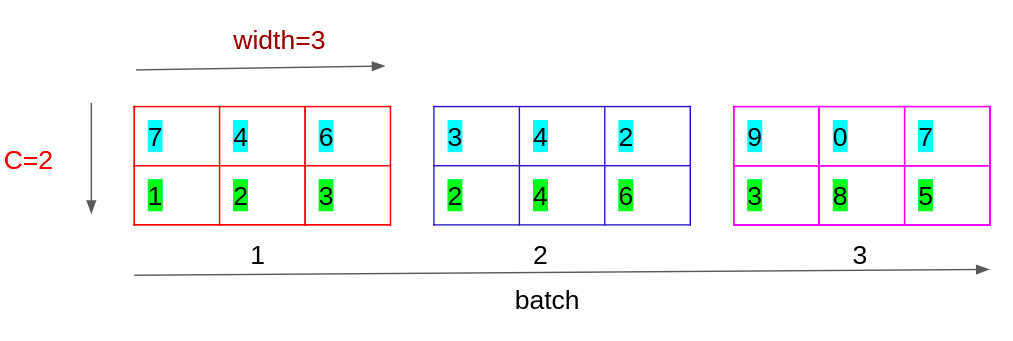
如上图,表示了一组NXCXL=3X2X3的数据,
使用BatchNorm1d后的输出为:
from torch import nn
batch = nn.BatchNorm1d(2, affine=False)
t = torch.tensor([[[7,4,6],[1,2,3]],[[3,4,2],[2,4,6]],[[9,0,7],[3,8,5]]])
t = t.float()
batch(t)
"""
输出为:
tensor([[[ 0.8750, -0.2500, 0.5000],
[-1.3250, -0.8480, -0.3710]],
[[-0.6250, -0.2500, -1.0000],
[-0.8480, 0.1060, 1.0600]],
[[ 1.6250, -1.7500, 0.8750],
[-0.3710, 2.0140, 0.5830]]])
"""
上述的计算过程等价为:
因为affine=False因此Batch计算的,等价为
在特征维度0上的均值
同理可计算方差为:‵Var(X) = 2.6667`
tmp = t[:,0,:]
print(tmp.mean())
print(tmp.var(unbiased=False).sqrt())
print((tmp-tmp.mean())/(tmp.var(unbiased=False).sqrt()+1e-5))
"""
Output:
tensor(4.6667)
tensor(2.6667)
tensor([[ 0.8750, -0.2500, 0.5000],
[-0.6250, -0.2500, -1.0000],
[ 1.6250, -1.7500, 0.8750]])
"""
注意在上述计算方差的过程中没有使用Bessel’s correction贝塞尔校正,除以的是n而不是n-1,因此通过这种方式计算的方差是有偏的。上面的结果与BatchNorm1d的输出是一致的。
# 2.BatchNorm2d
from torch import nn
batch = nn.BatchNorm2d(2, affine=False)
img = torch.randint(0, 255, (2,2,3,3))
img = img.float()
print(img)
print(batch(img))
t = img[:,0,:,:]
print(t.mean())
print(t.var().sqrt())
print((t-t.mean())/(t.var(unbiased=False).sqrt()+1e-5))
"""
Output:
tensor([[[[ 97., 163., 130.],
[ 26., 83., 183.],
[165., 108., 242.]],
[[113., 184., 236.],
[159., 223., 247.],
[ 48., 104., 111.]]],
[[[110., 93., 115.],
[237., 168., 120.],
[149., 115., 48.]],
[[117., 22., 43.],
[202., 63., 209.],
[104., 135., 99.]]]])
tensor([[[[-0.6115, 0.5873, -0.0121],
[-1.9012, -0.8658, 0.9506],
[ 0.6236, -0.4117, 2.0223]],
[[-0.3169, 0.7350, 1.5054],
[ 0.3646, 1.3128, 1.6683],
[-1.2798, -0.4502, -0.3465]]],
[[[-0.3754, -0.6842, -0.2846],
[ 1.9315, 0.6781, -0.1938],
[ 0.3330, -0.2846, -1.5016]],
[[-0.2576, -1.6650, -1.3539],
[ 1.0016, -1.0576, 1.1054],
[-0.4502, 0.0091, -0.5243]]]])
tensor(130.6667)
tensor(56.6486)
tensor([[[-0.6115, 0.5873, -0.0121],
[-1.9012, -0.8658, 0.9506],
[ 0.6236, -0.4117, 2.0223]],
[[-0.3754, -0.6842, -0.2846],
[ 1.9315, 0.6781, -0.1938],
[ 0.3330, -0.2846, -1.5016]]])
"""
BatchNorm2d的输入维度是NCHW形式的4维变量,计算均值和方差时是以C为标准逐各通道上计算的,每个通道上有一个均值和方差。在NHW上进行计算。
# 3.BatchNorm3d
batch = nn.BatchNorm3d(2, affine=False)
t = torch.randint(0, 3, (2,2,3,3,3))
t = t.float()
print(batch(t))
tmp = t[:,0,:,:,:]
print(tmp.mean())
print(tmp.var().sqrt())
print((tmp-tmp.mean())/(tmp.var(unbiased=False).sqrt()+1e-5))